A generation in computer terms refers to a shift in the technology that a computer uses or was using. At first, different hardware technologies were distinguished using the term “generation.” In the modern era, generation encompasses both the software and hardware that together comprise a computer system.
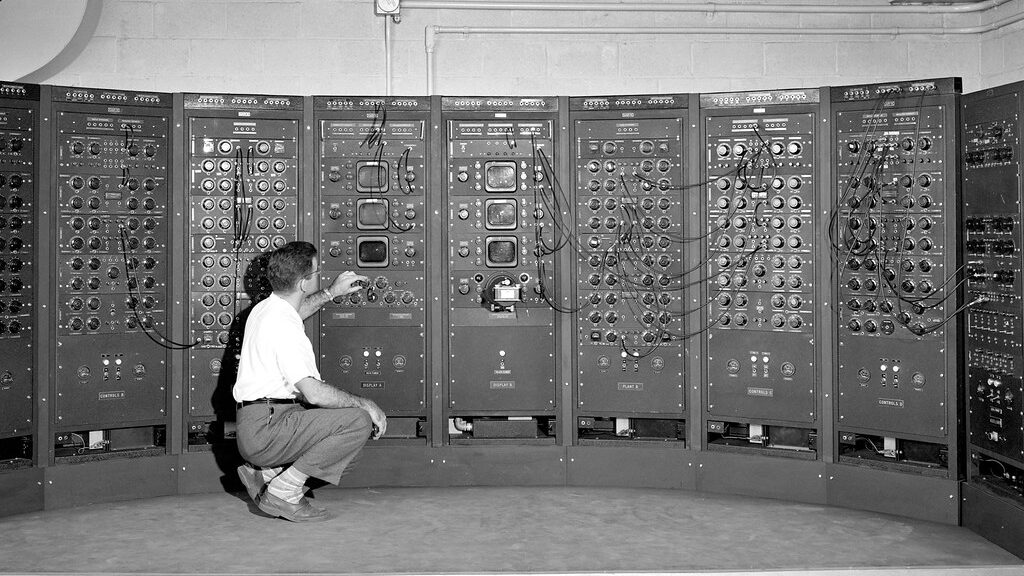
Table of Contents
Generation of Computers
- First Generation (1940s-1950s): Vacuum Tubes
- The first generation of computers, which emerged in the 1940s and lasted into the early 1950s, were gigantic machines built with vacuum tubes and other electronic components. These computers were enormous in size and required a lot of electricity to operate. They were also quite slow compared to modern standards.
- Imagine a room filled with large cabinets, each containing many vacuum tubes and other intricate parts. These computers were mainly used for tasks like complex calculations and solving scientific problems. They didn’t have screens or keyboards like today’s computers. Instead, programmers had to input instructions using punch cards, and the results were usually printed on paper.
- Due to their size, complexity, and limited capabilities, the first-generation computers were not very user-friendly and were primarily used by scientists, researchers, and governments for specific calculations. Despite their limitations, these early computers laid the foundation for the rapid advancements in technology that followed, leading to the development of smaller, faster, and more powerful computers in the years to come.
- Second Generation (1950s-1960s): Transistors
- Key features of second-generation computers include:
- Transistors: These tiny electronic components acted as switches and amplifiers, making the computer’s operations faster and more reliable.
- Smaller Size: With the use of transistors, computers became smaller, which allowed them to be used in more practical settings.
- Faster Speed: The use of transistors improved the processing speed of these computers, enabling them to perform calculations more quickly.
- Magnetic Core Memory: Second-generation computers used magnetic core memory for storage, which was more reliable and faster than the earlier memory technologies.
- Assembly Language and High-Level Languages: Programming became a bit more user-friendly with the development of assembly languages and high-level programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN.
- Batch Processing: Computers were still primarily used in batch processing mode, where a series of jobs were submitted and processed one after the other.
- Key features of second-generation computers include:
- Third Generation (1960s-1970s): Integrated Circuits (ICs)
- The third generation of computers represented another significant leap in technology and took place during the 1960s to the 1970s. This era introduced integrated circuits (ICs), which allowed multiple transistors and other components to be packed onto a single semiconductor chip. Here’s what defined the third generation of computers:
- Integrated Circuits: Instead of individual transistors and other components, third-generation computers used integrated circuits, also known as chips. These chips contained thousands of transistors and other elements, making computers even smaller, more powerful, and more reliable.
- Smaller and More Powerful: The integration of components on a chip allowed computers to become smaller, more efficient, and capable of performing more complex tasks.
- High-Level Languages and Timesharing: Third-generation computers saw further advancements in programming languages like COBOL, FORTRAN, and the development of more user-friendly languages like BASIC. Timesharing systems also emerged, allowing multiple users to interact with the same computer simultaneously.
- Operating Systems: The concept of an operating system became more refined in this generation. These systems managed computer resources and allowed users to interact with the computer through a more intuitive interface.
- Remote Data Entry and Output: Users could now access computers from remote locations and submit jobs or retrieve data, laying the groundwork for later developments in networking.
- Storage Improvements: Magnetic disk storage systems became more common, providing faster and more reliable data storage compared to earlier magnetic core memory.
- Advancements in Graphics and User Interaction: Third-generation computers started incorporating rudimentary graphics capabilities and interactive elements, making them more suitable for business and educational applications.
- Minicomputers: With the increased use of integrated circuits, smaller computers known as minicomputers became accessible to businesses, universities, and research institutions. These were less powerful than mainframes but still offered considerable computing power.
- The third generation of computers represented another significant leap in technology and took place during the 1960s to the 1970s. This era introduced integrated circuits (ICs), which allowed multiple transistors and other components to be packed onto a single semiconductor chip. Here’s what defined the third generation of computers:
- Fourth Generation (1970s-1980s): Microprocessors
- The fourth generation of computers, spanning from the late 1970s to the early 1990s, brought about remarkable advancements in technology, leading to the birth of modern personal computing. Here’s what defined the fourth generation:
- Microprocessors: The most revolutionary development of this era was the invention of microprocessors. These are complete central processing units (CPUs) on a single chip, integrating millions of transistors. Microprocessors made computers much smaller, faster, and more accessible to individuals.
- Personal Computers (PCs): The introduction of microprocessors paved the way for the widespread adoption of personal computers. Brands like Apple and IBM produced computers that were compact enough for home and small office use, revolutionizing how people interacted with technology.
- Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs): GUIs, like the iconic interface of the Apple Macintosh, made computers more user-friendly. These interfaces used icons, windows, and pointers, enabling users to interact with computers using a mouse and visually intuitive controls.
- Software Applications: A wide range of software applications became available for personal computers, including word processors, spreadsheets, and graphics software. This made computers more versatile and useful for various tasks.
- Networking and the Internet: The late fourth generation saw the establishment of computer networking protocols and the beginning of the internet. This development laid the foundation for global connectivity and information sharing.
- Storage Advancements: Hard disk drives became more common and offered significantly increased storage capacity. Floppy disks and later compact discs (CDs) also provided removable storage options.
- Fifth-Generation Languages: High-level programming languages continued to evolve, and fifth-generation languages (such as Prolog) emerged, focusing on artificial intelligence and natural language processing.
- Laptops and Portability: Towards the end of the fourth generation, laptops were introduced, offering the convenience of computing on the go.
- Video Games and Entertainment: This era also witnessed the rise of video game consoles and home gaming systems, marking the beginning of the video game industry as we know it today.
- The fourth generation of computers was marked by the democratization of computing, making technology accessible to individuals and transforming how people worked, communicated, and entertained themselves. The advent of microprocessors and personal computers set the stage for further innovations in subsequent generations.
- The fourth generation of computers, spanning from the late 1970s to the early 1990s, brought about remarkable advancements in technology, leading to the birth of modern personal computing. Here’s what defined the fourth generation:
- Fifth Generation (1980s-Present): Artificial Intelligence
- The fifth generation of computers, which began in the late 1980s and extends to the present day, is characterized by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and parallel processing. Here’s what defines the fifth generation:
- Parallel Processing: Fifth-generation computers utilize parallel processing, where multiple processors work together to solve complex problems simultaneously. This significantly increases computing power and speed.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The fifth generation is closely associated with the development of AI. Computers in this era are capable of processing large amounts of data and learning from it, enabling them to perform tasks that previously required human intelligence, like natural language understanding, image recognition, and decision-making.
- Expert Systems: Expert systems are a type of AI software that emulates the decision-making abilities of a human expert in a specific domain. These systems can provide recommendations, diagnose issues, and assist with complex problem-solving.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Computers of this generation have made significant strides in understanding and generating human language. This has led to the development of virtual assistants, chatbots, and language translation tools.
- Massive Data Storage and Processing: The fifth generation witnessed an explosion in data generation and storage. Advances in storage technology, along with sophisticated data processing techniques, allowed for the handling of vast amounts of information.
- Networking and the World Wide Web: The internet and the World Wide Web (WWW) became widespread during this generation. The ability to connect computers globally transformed communication, commerce, and information sharing.
- Multimedia Capabilities: Computers gained the ability to handle multimedia content, such as images, videos, and sound. This led to developments in fields like digital media production, entertainment, and virtual reality.
- Miniaturization and Mobility: Alongside the advances in AI, computers became smaller, lighter, and more portable. Laptops, tablets, and smartphones emerged, enabling computing on the go.
- Cloud Computing: The concept of cloud computing became popular in this generation, allowing users to access and store data and software over the internet, rather than relying solely on local resources.
- Quantum Computing (Emerging): Towards the latter part of the fifth generation, the field of quantum computing began to show promise. Quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to perform certain types of calculations exponentially faster than classical computers.
- The fifth generation of computers is characterized by the fusion of AI, advanced networking, and an emphasis on data processing and interpretation. These developments continue to shape our world, impacting everything from how we interact with technology to how industries operate and innovate.
- The fifth generation of computers, which began in the late 1980s and extends to the present day, is characterized by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and parallel processing. Here’s what defines the fifth generation:
Each generation brought about significant advancements in computer technology, leading to faster processing, reduced size, increased reliability, and expanded capabilities. Alongside these generations, other key concepts you might encounter in your studies include:
- Moore’s Law: An observation that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles about every two years, leading to exponential growth in computing power.
- Programming Languages: Different generations introduced new programming languages. Understanding languages like FORTRAN, COBOL, BASIC, C, Java, and Python can help you appreciate the evolution of software development.
- Operating Systems: Systems like DOS, Windows, Unix/Linux, and macOS are essential to understand how computers manage resources and run software.
- Storage Evolution: From punch cards and magnetic tapes to hard drives and solid-state drives, the way we store and access data has evolved significantly.
- Networking: The development of the Internet and networking protocols transformed the way computers communicate and share information.
Remember, each generation built upon the previous one, and understanding this evolution will give you a solid foundation in computer science and technology.
Who was the father of Computer ?
The first mechanical Computer was introduced by Charles Babbage in 1837. It was also called as Analytical Engine. Charles Babbage is known as father of computer.

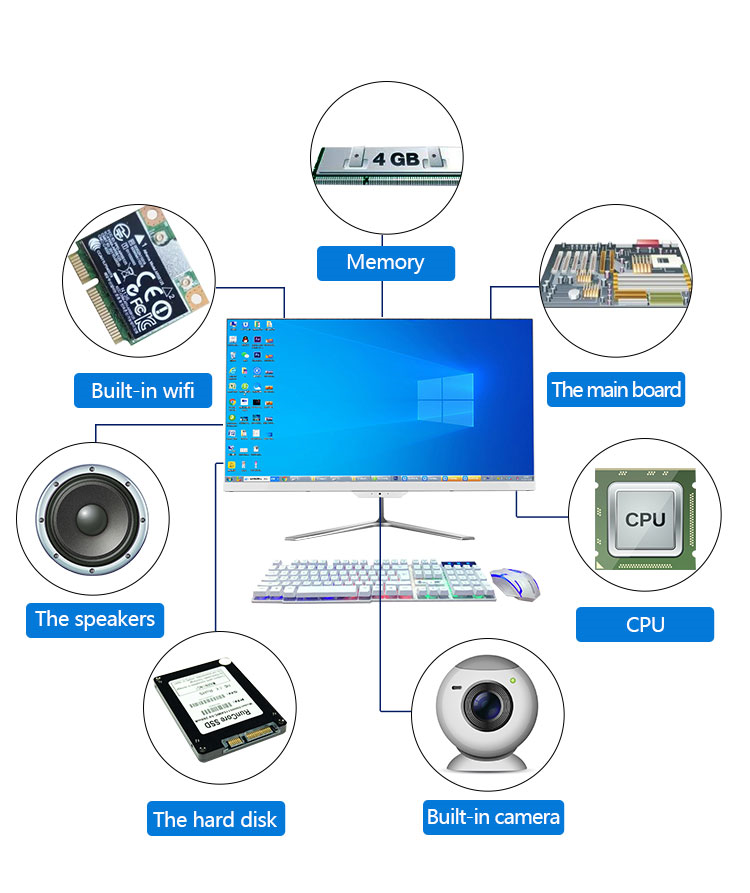
Latest Generation of computer 2023: As Below Picture
Now a Days , Latest 12th and 13th Generation Processor of intel/AMD is available in Computer Market.-intel i3, intel i5 , intel i7 and intel i9. These are in two variant-Mobile and Desktop
Who invented computer ?
Charles Babbage is known as father of computer,The first mechanical Computer was introduced by Charles Babbage in 1837
What is full form of computer ?
It is an electronics device which take input from input and
and hat can be programmed to accept some inputs in terms of data,
What is computer in Hindi ?
एक ऐसा इलेक्ट्रॉनिक उपकरण है जो यूजर की कमांड पर इनपुट को प्रोसेस करके आउटपुट में बदलता है एवं गणना को आसान बनाता है
What is computer system ?
It is an electronics device which take input from input and
and hat can be programmed to accept some inputs in terms of data,
What is network in Computer ?
When two or more than two computer are
connected to each other, In a way to transfer data from
two or more than two computers . it is called network
Many types of network can be possible like-LAN,MAN, WAN, Ethernet.
How to take screenshot on computer
Just click on Print Screen on keyboard when system is on.
Automatically capture the screen shot and paste on any word
